Introduction
In our modern world, we are constantly surrounded by various environmental noises that can have a significant impact on our health and well-being. In 2011, an estimated one million healthy life years were lost from traffic-related noise in the western part of Europe only. Therefore,understanding the noise level of common sounds is crucial in order to mitigate their harmful effects. This article will delve into the classification of environmental noise as well as the potential dangers that excessive noise exposure can pose to our health.

the Noise Level of Environmental Sound
Common environmental noise levels constitute a diverse spectrum of auditory experiences that shape our daily lives. From the gentle hum of household appliances to the thunderous roar of construction machinery, the range of noise sources we encounter is vast and varied.
Road traffic noise, a ubiquitous presence in urban settings, typically hovers between 70 to 85 decibels (dB) during regular traffic flow, punctuating our surroundings with a consistent background din. Meanwhile, construction sites reverberate with noise levels that can soar to 100 dB or more, disrupting the tranquility of neighborhoods and workplaces alike. Indoors, the cacophony of everyday appliances like vacuum cleaners and blenders contributes to ambient noise levels ranging from 60 to 80 dB, creating a constant auditory backdrop within our living space.
-
Points of reference measured in decibels
0 The softest sound a person can hear with normal hearing
10 normal breathing
20 whispering at 5 feet
30 soft whisper
50 rainfall
60 normal conversation
110 shouting in ear
120 thunder
Understanding the nuances of these noise level of common sounds is vital for assessing their potential impact on our health and well-being. By identify noise levels affecting health that surround us, we can take proactive measures to mitigate excessive noise exposure and safeguard our auditory health for the future.Continued exposure to noise above 70 dBA (adjusted decibels) over time will cause hearing loss. The volume (dBA) and the length of exposure to the sound will tell you how harmful the noise is. In general, the louder the noise, the less time required before hearing loss will occur.
Health Hazards of Environmental Noise
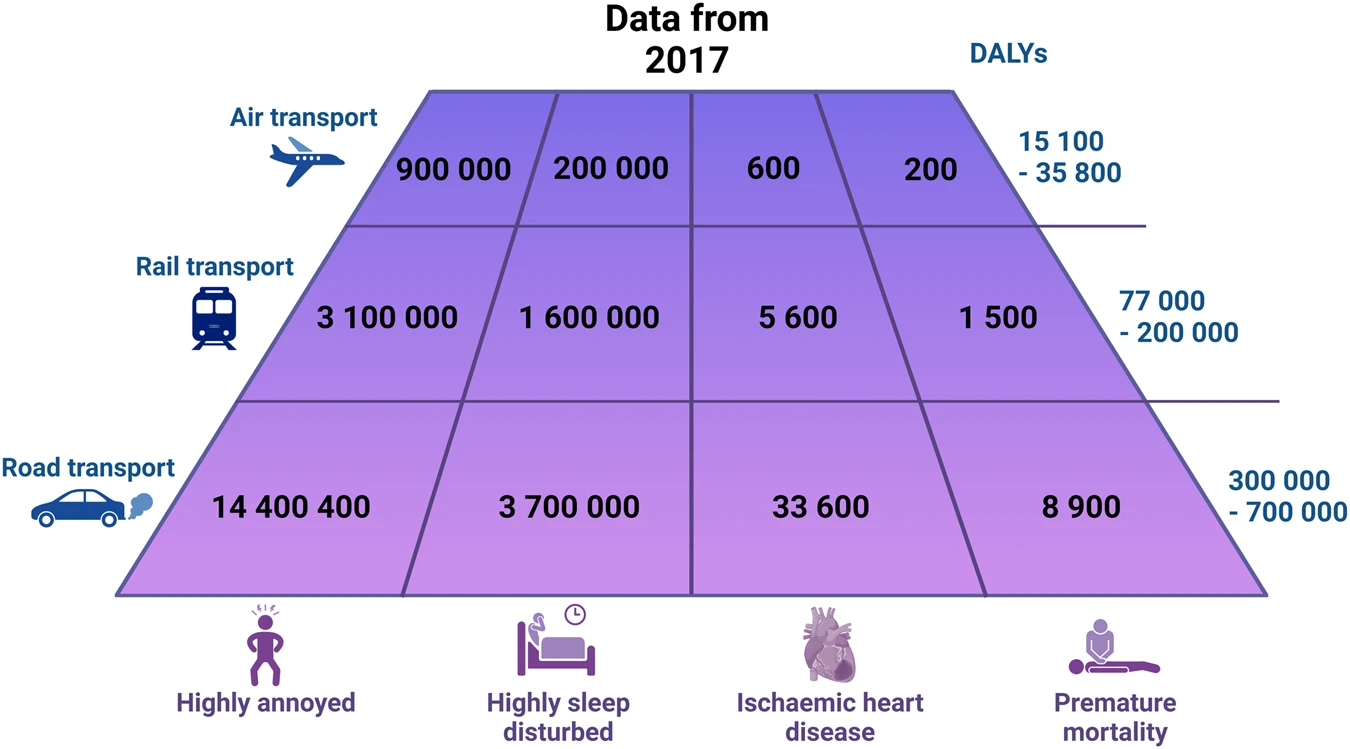
Researchers and clinicians have found that noise pollution not only drives hearing loss, tinnitus, and hypersensitivity to sound, but can cause or exacerbate cardiovascular disease; type 2 diabetes; sleep disturbances; stress; mental health and cognition problems, including memory impairment and attention deficits; childhood learning delays; and low birth weight. Moreover, different types of noise can cause different health hazards. Taking hearing loss as an example, prolonged exposure to loud noise, especially at levels above 85 decibels (dB), can cause irreversible damage to the auditory system, leading to hearing loss.
Assistance of Hearing Aids for Noise-Induced Hearing Loss
For individuals affected by noise-induced hearing loss, hearing aids serve as essential devices that amplify sounds, reduce background noise, enhance communication, and ultimately improve their quality of life. By utilizing advanced technology and personalized solutions, hearing aids can help individuals regain clarity in auditory perception and navigate challenging listening environments with greater ease and confidence.
Ideal for individuals with hearing loss at any level, Nearity Hearpod Air shines with its advanced noise-cancelling technology that reduces unwanted sounds, enabling you to concentrate on what truly matters. Moreover, it provides 4 audio processing algorithms that are customizable to accommodate diverse needs. For added convenience, it is worn as a single piece, reducing the risk of misplacement, and allows independent volume adjustment for each ear. With its excellent design, Nearity HearPod Air is a great match for this target users, to perfectly address your noise-induced hearing loss.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is essential to be aware of the different types of environmental noise and their potential impact on our health. By understanding the sources of noise pollution and taking proactive measures to reduce exposure, we can minimize the risks associated with excessive noise levels. If your hearing has unfortunately been impaired by noise, ask for help from Nearity HearPod Air. Additionally, Nearity offers complimentary online hearing tests. If you need this service, please contact marketing@nearity.co





